As a polymer synthetic material, geomembrane has excellent anti-seepage and isolation properties, and plays a vital role in the construction and operation of landfills.
Application scenarios
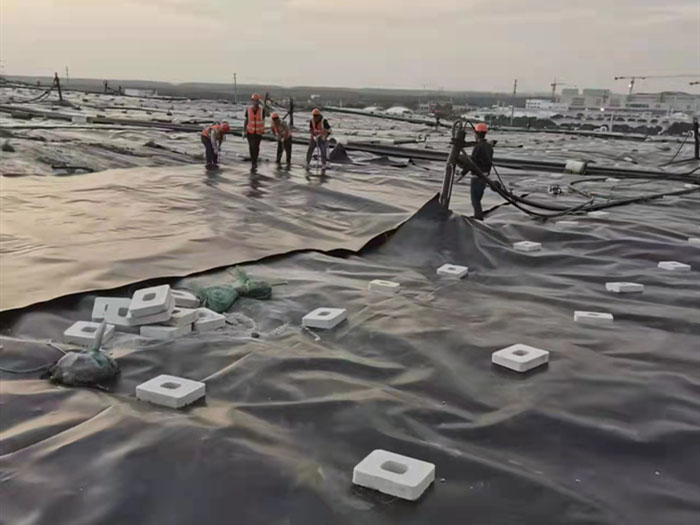
1. Bottom liner system: Geomembrane is laid at the bottom of the landfill to form a reliable anti-seepage barrier to prevent the infiltration of garbage leachate and pollute groundwater and soil. Usually, a non-woven geotextile is laid under the geomembrane as a protective layer to prevent sharp objects from piercing the geomembrane; a drainage layer, garbage layer, etc. are laid on top.
2. Slope covering system: Geomembrane is also needed to be laid on the slope of the landfill to prevent rainwater from infiltrating into the garbage pile from the slope and increasing the amount of leachate produced. The laying of slope geomembranes requires special fixing and protection measures to adapt to the slope and terrain changes of the slope.
Application advantages
1. High efficiency anti-seepage: Geomembranes have extremely low permeability coefficients, which can effectively prevent harmful substances in landfill leachate from penetrating into the ground, protecting groundwater resources and soil environment. For example, the permeability coefficient of HDPE (high-density polyethylene) geomembranes can reach below 10−12cm/s, which is much lower than the permeability of soil and other traditional anti-seepage materials.
2. Good chemical stability: The leachate in the landfill has complex components and contains a large amount of organic matter, inorganic salts, heavy metals and other corrosive substances. Geomembranes have good chemical stability and can resist the erosion of these substances, ensuring long-term performance.
3. Convenient construction: Geomembranes are soft and light, easy to transport and lay. Various connection methods such as welding and bonding can be used, with fast construction speed and short construction period, which can adapt to the requirements of different terrains and construction conditions.
4. Low cost: Compared with other anti-seepage materials, geomembranes are relatively cheap and have simple construction processes, which can reduce the construction cost of landfills. At the same time, due to its long service life, the maintenance cost is relatively low.
Construction points
1. Foundation treatment: Before laying geomembranes, the foundation surface must be treated to ensure that it is flat, solid, and free of sharp objects and debris. For soft soil foundations, reinforcement treatment is required to improve the bearing capacity and stability of the foundation.
2. Laying construction: The laying of geomembranes should follow a certain sequence and method to avoid wrinkles, bubbles and breakage. During the laying process, attention should be paid to the overlap width and connection quality of the geomembrane. Generally, hot melt welding or extrusion welding is used for connection to ensure the anti-seepage performance of the joints.
3. Anchoring and fixing: In order to prevent the geomembrane from displacement under the action of external forces such as wind and water flow, it needs to be anchored and fixed. The anchoring method can be anchoring trenches, anchoring plates, etc., and the anchoring depth and width should meet the design requirements.
4. Quality inspection: After the geomembrane is laid, a comprehensive quality inspection is required, including appearance inspection, thickness inspection, permeability coefficient inspection, joint strength inspection, etc. Only geomembranes that have passed the inspection can be put into use.
Common problems and solutions
1. Damage problem: During the construction process, the geomembrane may be punctured or scratched by sharp objects. The solution includes strengthening construction management to avoid operations that may cause damage above the geomembrane; laying a protective layer under the geomembrane, such as non-woven geotextiles; and repairing the damaged parts in time, which can be repaired by welding or bonding.
2. Seam leakage: If the seams of the geomembrane are not handled properly, it may cause leakage. The solution is to strictly follow the construction specifications for seam construction to ensure the quality of welding or bonding; conduct quality inspection on the seams, and rework and deal with leakage problems in time.
3. Settlement problem: During the use of the landfill, due to the compression and settlement of garbage, the geomembrane may be deformed or damaged due to tensile stress. The solution is to fully consider the settlement factors of garbage during design and reasonably determine the laying method and anchoring measures of geomembrane; during the landfill process, control the landfill speed and height of garbage to avoid excessive settlement differences.